COPQ Explained
The Business Lens for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Recovery
Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) is the unifying lens we use to quantify internal failure costs, prioritize actions, and measure results in pharmaceutical manufacturing operations.
Understanding Total Cost of Quality
Total Cost of Quality can be broken down into two categories: Cost of Good Quality (prevention and appraisal) and Cost of Poor Quality (internal and external failures). We focus on identifying the biggest cost drivers within COPQ to deliver measurable value.
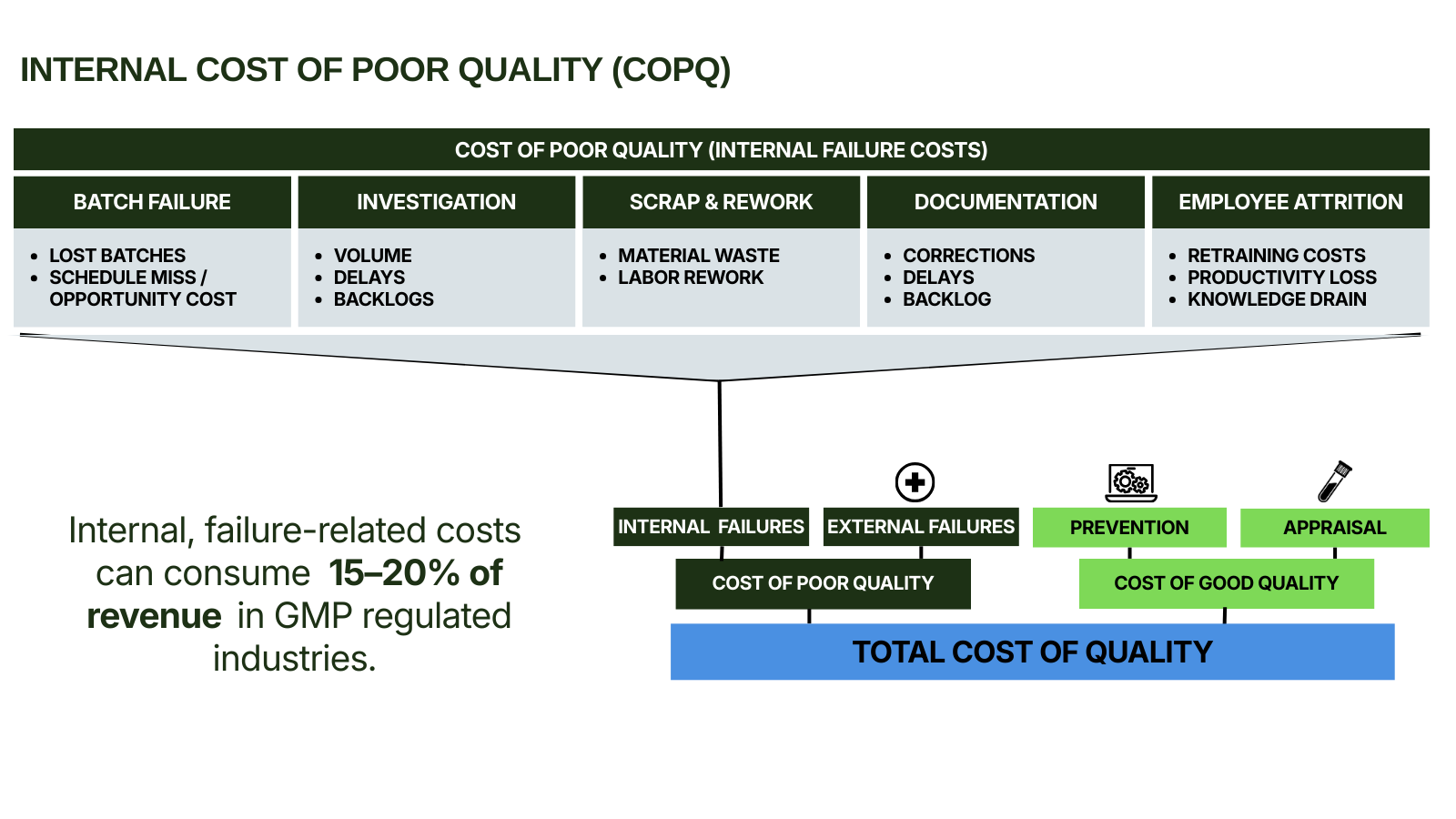
Cost of Good Quality
Investments in prevention and appraisal—the proactive costs of maintaining quality standards.
- Prevention: Training, process design, quality planning
- Appraisal: Testing, inspection, audits, calibration
Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)
The financial impact of failures—where we focus our recovery efforts to deliver rapid value.
- Internal Failures: Batch failures, rework, investigations, delays
- External Failures: Recalls, regulatory actions, customer complaints
How We Deliver Value:
We start by quantifying your Total Cost of Quality, then identify the biggest cost drivers within COPQ—typically internal failures like batch failures, deviation investigations, and documentation delays. We leverage the entire GMPKit Operating Model (diagnostics, readiness support, governance systems, and digital visibility) to systematically reduce these COPQ targets, delivering measurable results in 90-120 days.
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, internal failure costs typically represent 15-20% of revenue.
Understanding COPQ in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Explore how Cost of Poor Quality impacts pharmaceutical operations and how we systematically reduce internal failure costs.





The GMPKit COPQ Calculator
Our free COPQ calculator helps you quantify internal failure costs and model recovery scenarios—giving you the business case for rapid operational recovery.
100% Free
No registration required. No credit card. No sales pitch. Just a powerful tool to quantify your COPQ.
Email Reports
Generate a detailed PDF report and email it to yourself or share with your leadership team.
Multiple Scenarios
Model different recovery scenarios and compare the financial impact of various improvement strategies.
What You'll Get:
- Quantified internal failure costs across batch failures, investigations, rework, and documentation delays
- COPQ as a percentage of revenue to benchmark against industry standards (15-20%)
- Scenario modeling to estimate ROI from operational recovery initiatives
- Shareable PDF report for leadership presentations and business case development
How COPQ Guides Our Approach
COPQ is not just a metric—it's the lens we use to prioritize actions, measure progress, and demonstrate ROI throughout our 90-120 day operational recovery engagements.
Prioritization
We use COPQ to identify which failures are costing you the most—focusing recovery efforts on the highest-impact areas first.
Progress Tracking
COPQ reduction becomes the primary KPI for measuring operational recovery—translating process improvements into financial impact.
ROI Demonstration
By quantifying COPQ before and after our engagement, we demonstrate clear ROI that justifies the investment in operational recovery.
Executive Communication
COPQ provides a common language for operational teams and executives—translating technical problems into business impact.
Ready to Quantify Your COPQ?
Start with the free COPQ Calculator to understand your internal failure costs, or schedule a discovery call to discuss how we can help you execute rapid operational recovery in 90-120 days.
